Csrf Report
CSRF Vulnerabiltiy Report
Table of Contents
- Outline
- Vulnerabiltiy Explanation
- Proof of Concept - Simulating a Phishing Attack
- Source Code Analysis -
- Mitigating CSRF Attacks
Outline
The goal of this write-up is to document and demonstrate CSRF (Cross Site Request Forgery) attacks performed against the Damn Vulnerable Web Application (DVWA). The objective of this attack was to change the password of the admin account through CSRF attack.This report mocks a penetration testing report and a debriefing situation to a client.
Vulnerabiltiy Explanation
CSRF is an attack where the attacker causes the victim user to carry out an action unintentionally while that user is authenticated. This can disrupt normal user expereince, lead to data manipulation, deletion, and at times account takeovers. Depending on the account privilege, an attack could lead to a full control over a application system. CSRF attacks often involve social engineering techniques such as tricking the user to click on a malicious link. There are several prerequisites for an CSRF attack to be successful. The user has to be already logged into the application using cookie based sessions without proper CSRF defence in place. The user has to be tricked to conduct some action such as clicking on a malicious link.
| Information | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Name | CSRF |
| Severity | High |
| CVSS | 8.3 |
| Path | http://127.0.0.1/vulnerabilities/exec/ |
The base CVSS was calculated upon the following metrics.
| Base Metrics | Explanations |
|---|---|
| Attack Vector (AV) | Network(N) The vulnerability can be exploited remotely over a network connection. |
| Attack Complexity (AC) | Low (L) The vulnerability is straightforward and requires minimal or no special knowledge. |
| Privilege Required (PR) | Low (L) The attack requires some privilege. The user has to login to DVWA webpage to conduct the exploit |
| User Intercation (UI) | Required (R) The vulnerability needs user interaction. |
| Scope (S) | Unchanged(S:U) An exploit can only affect the specific system |
| Confidentiality Impact (C) | Medium (M) The vulnerability has medium impact on the confidentiality of information. |
| Integrity Impact (I) | High (H) The vulnerability has a signigicant impact on the integrity of the information |
| Availability Impact (A) | High (H) The vulnerability has a significant impact on the availability of the system or resource. |
Proof of Concept
DISCLAIMER Law Enforcement Impersonatation is a serious crime. This POC was conducted in a virtual environment and was self tested. Even in real red teaming engagement, law enforcement impersonation is at most times not allowed. The malicious email only targets DVWA website for POC.
For proof of concept (POC), the tester has simulated a phishing attack to conduct a CSRF attack. In the email, the tester has impersonated an authoritive figure to entice the victim on clicking a link. Upon clicking the link, the authenticated DVWA victim user is redirected to a malicious website that has copied (iframed) another website. Here the victim’s password is changed unintentionally without notice. After vising the site, the victim user admin cannot login with the same password anymore because it has been unintentionally changed.
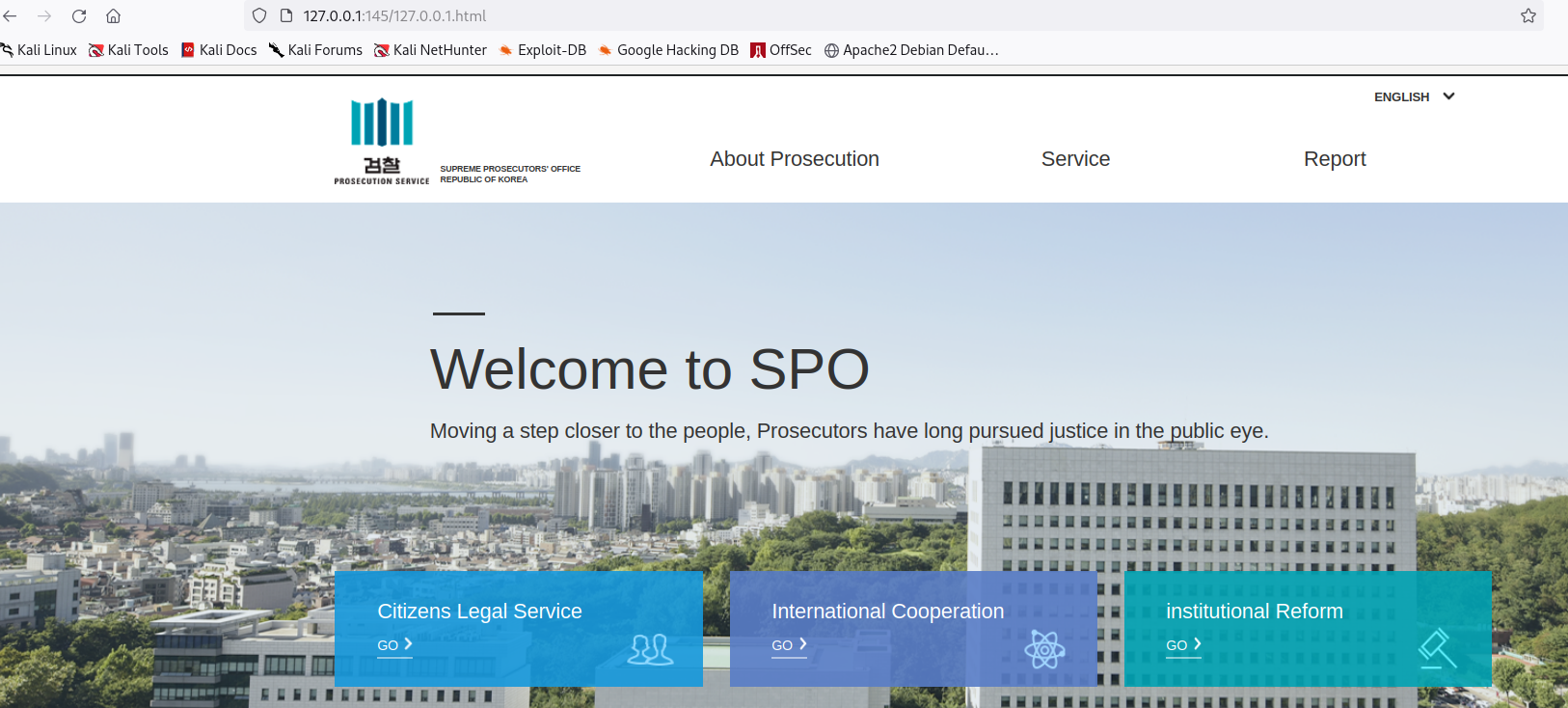
Hosting a Malicious Website
Firstly, the tester crafted an HTML that could conduct the CSRF attack. The base HTML was mainly made through the use of an iframe to embed a real website, in this case, a Prosecution Service webpage. Moreover, the tester used the <img src=""> HTML tag to perform the malicious action of changing the password.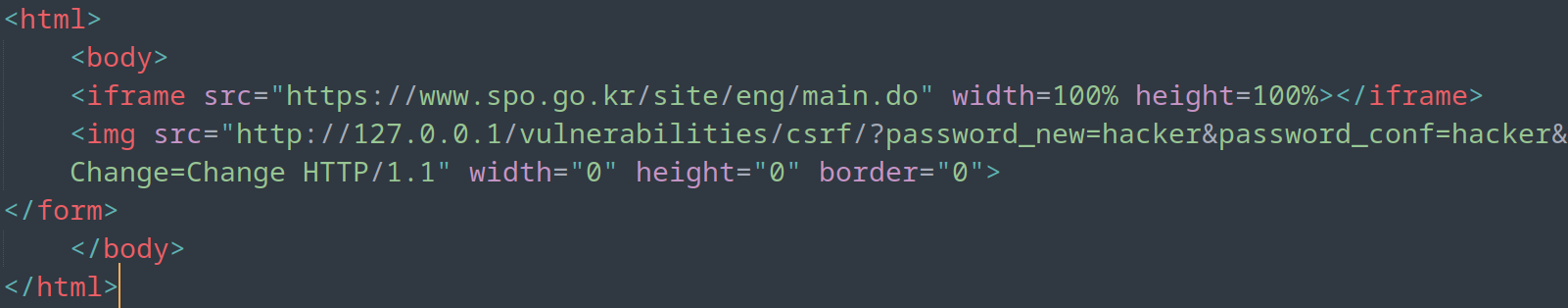 Finally, the tester hosted a Python server to host the malicious website.
Finally, the tester hosted a Python server to host the malicious website.
python3 -m http.server 145
Creating a Phishing Email
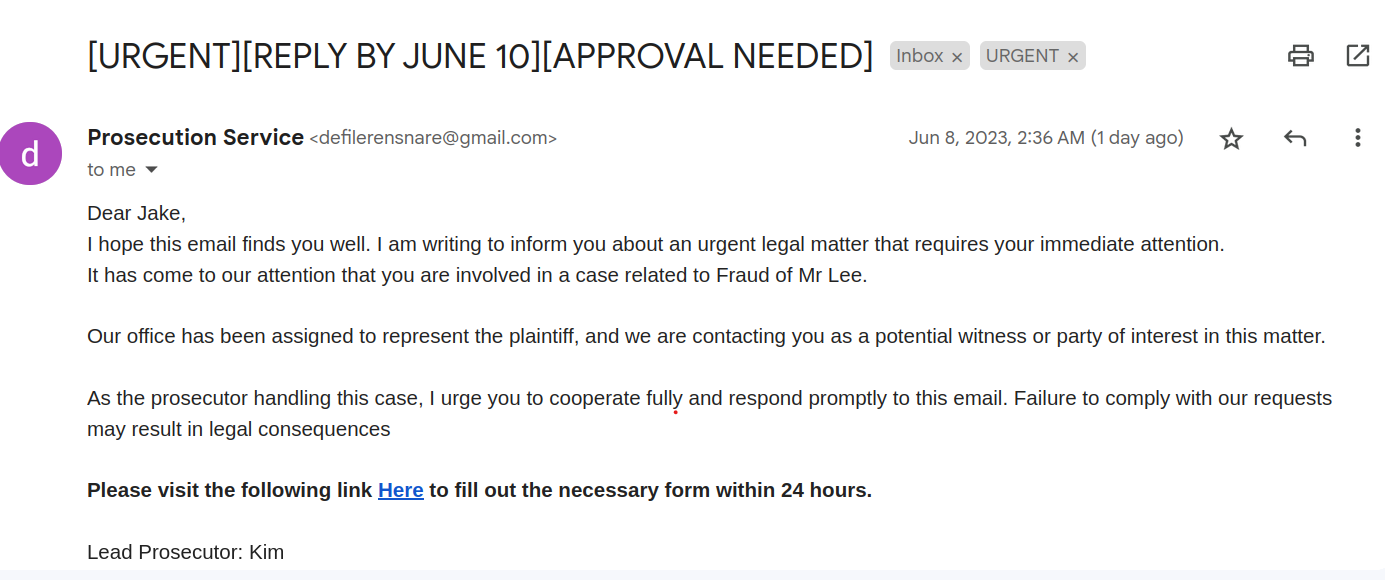
The tester also crafted a simple phising email that impersonated an authoritive figure with the help of ChatGPT. The tester made sure that the email consisted of a sense of urgency, time pressure, threats of legal action and a sense of authority in the email. In crafting the email, the tester first modified the sender’s name as an authority figure. This could be done by logging into gmail, navigating to Accounts and Imports and changing the Send Mail as. Next upon crafting the email, the tester utilized the gmail link function to hide the orginal hosted webpage to a simple clickable Link.
Demonstration
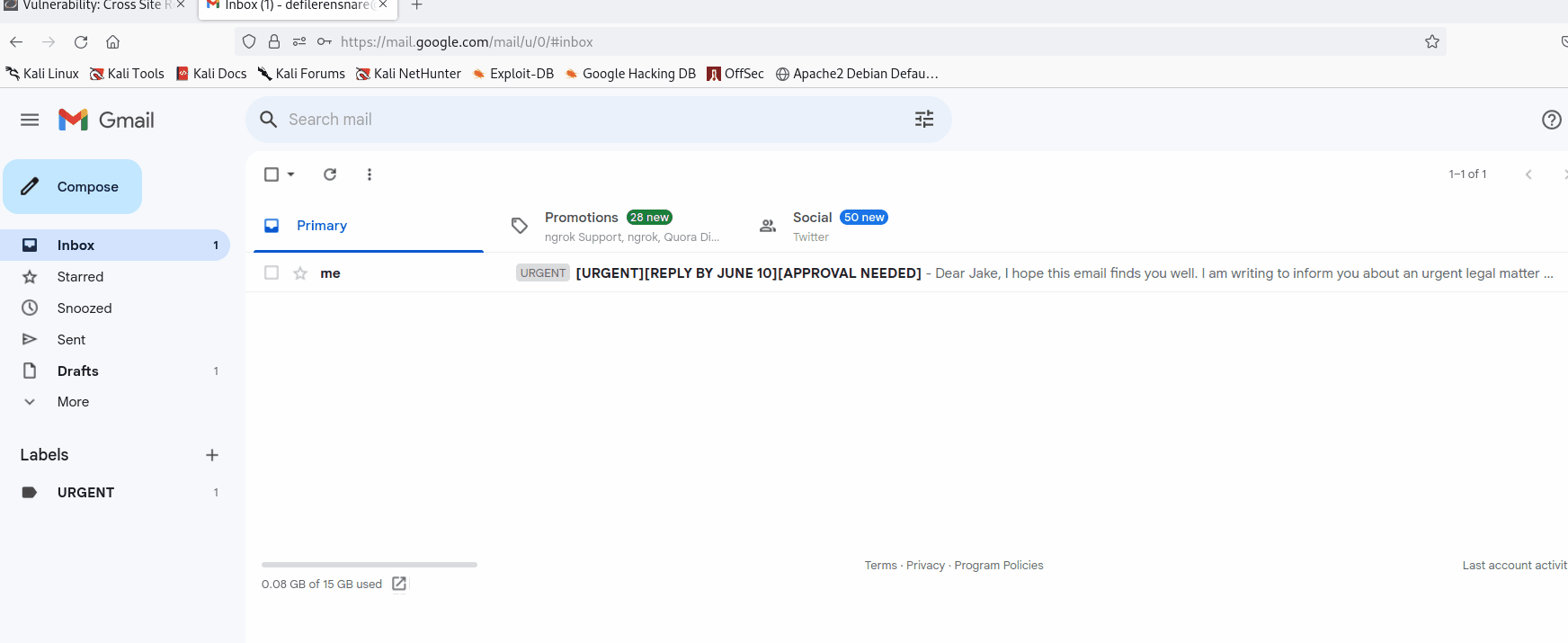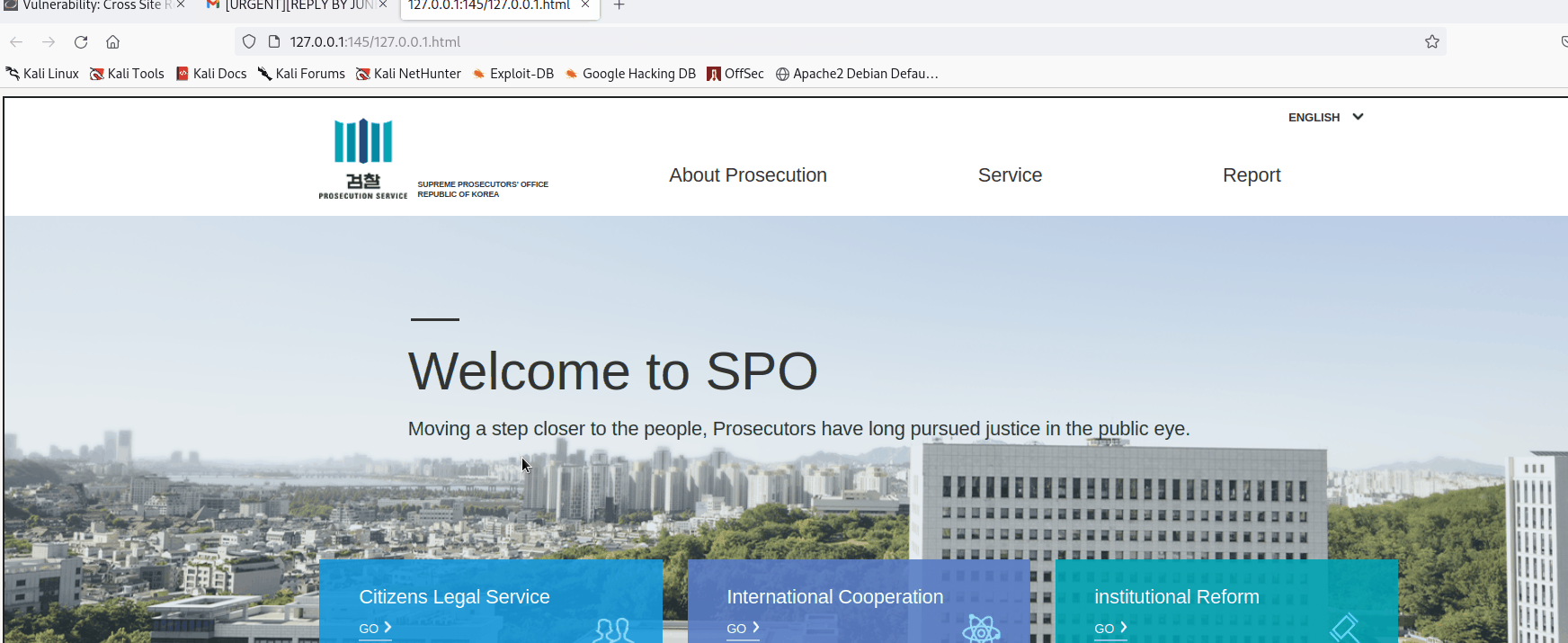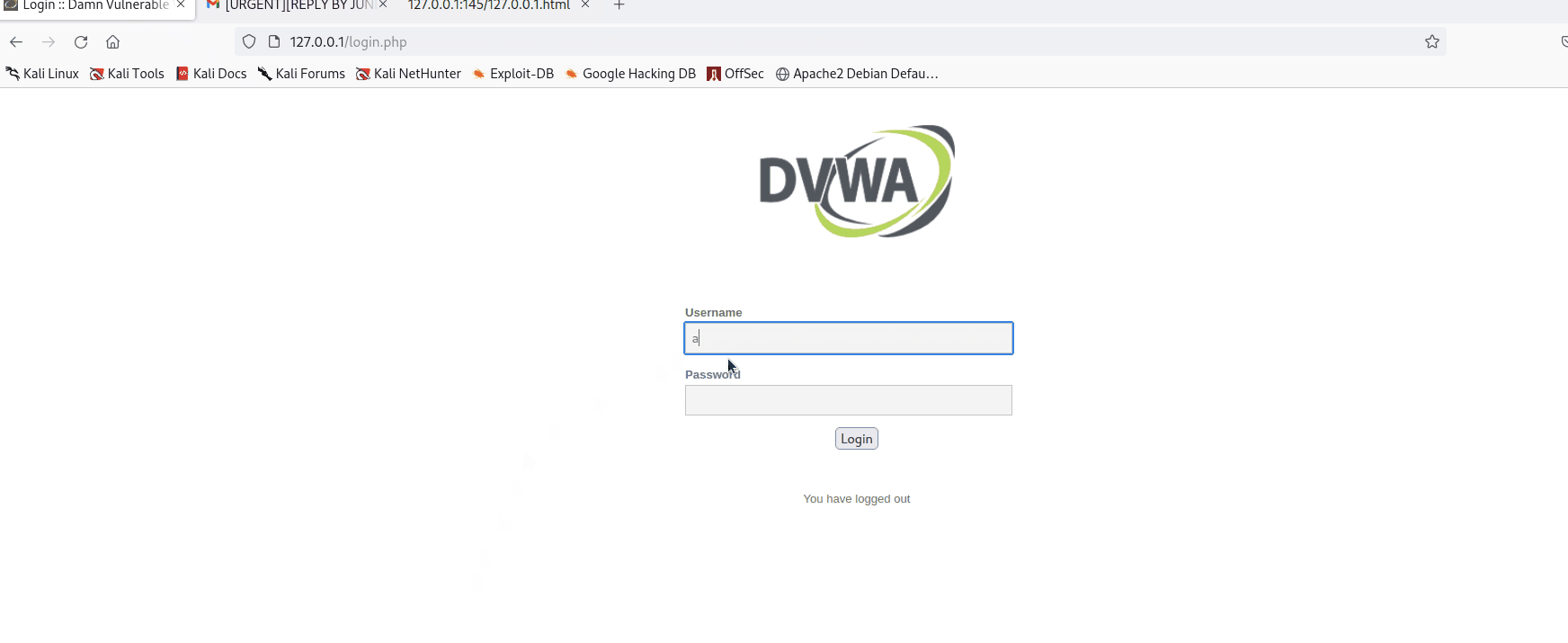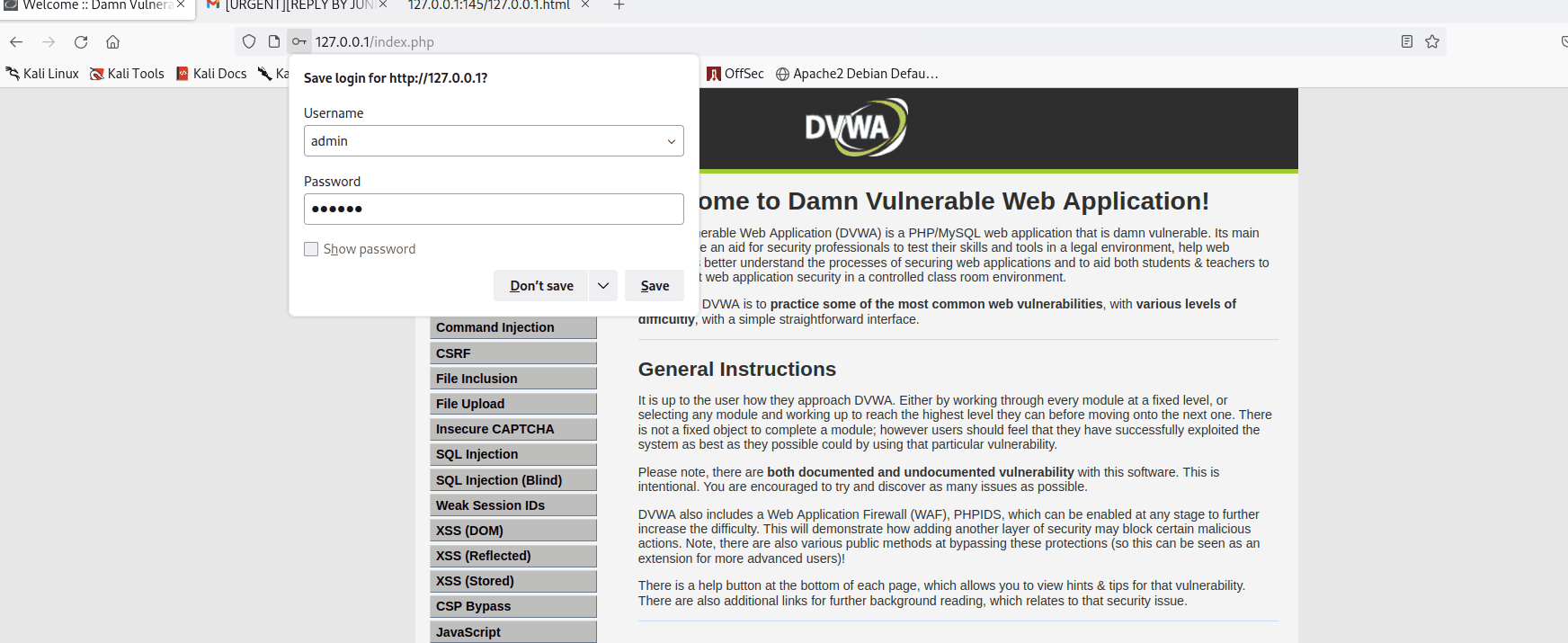
However, there is a lot of room for improvement in this simulated attack. For instance, the email could have been enhanced by hiding the sending email address or by using a seemingly more realistic email address by purchasing a domain. Additionally, further study is needed to make the link URL less suspicious.
Source Code Analysis
In the Security-Low-Level module, the testers figured out that the website had significant vulnerabilities when the change password request was intercepted. These vulnerabilities included the usage of the GET method, reliance on cookie-based sessions, and most importantly, the absence of any CSRF token implementation. Specifically, the use of the GET method exposes the transmitted data in the URL, which allowed the tester to view sensitive information and manipulate it.
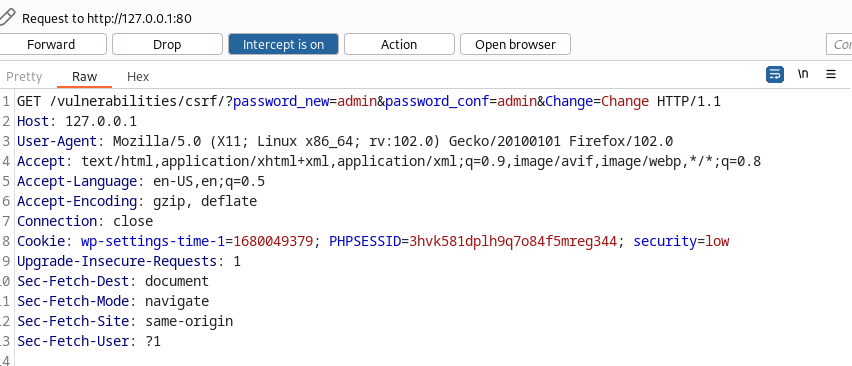
For example, in the interception of /vulnerabilities/csrf/?password_new=admin&password_conf=admin&Change=Change, the password change request’s sensitive data, such as the new password, was clearly visible in the URL. This exposed various avenues for the tester such as embedding this password change request in a malicous website as seen above. To mitigate this risk, it is recommended to use the more secure POST method when submitting sensitive data.
Furthermore, despite the website utilizing cookies for session management, it lacked proper prevention mechanisms like CSRF tokens to validate and block unauthorized changes. This omission allowed the tester to manipulate requests on behalf of the users when they visited the website.
In the Security-Medium-Level module the tester figured out that the website was using a Referer to check the origin of the request. That is, if the request was not made from the origin, the tester would not be able to make any changes to the account. This can be seen in burpe suite, where there is a new Referer section in the header.
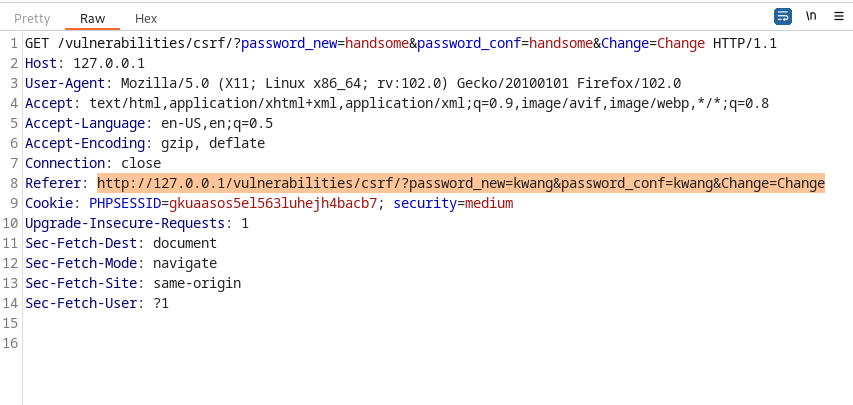 Moreover, analzying the source code, it can be seen that the php code checks if the
Moreover, analzying the source code, it can be seen that the php code checks if the Referer contains the servername. if( stripos( $_SERVER[ 'HTTP_REFERER' ] ,$_SERVER[ 'SERVER_NAME' ]) !== false )
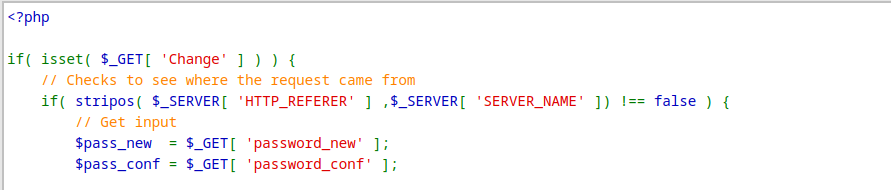 However, this prevention method was bypassable, as the tester could simply add the sever name to the malicious url to bypass this defense method.
However, this prevention method was bypassable, as the tester could simply add the sever name to the malicious url to bypass this defense method.
In the Security-High-Level module there are CSRF token measures and Cross origin request block, same origin Policy (SOP). This prevents java script code from making a cross origin request.
Mitigating CSRF Attacks
Zero Trust:
Educate Employers about the dangers of clicking unknown links in emails. Check if the email is sent from a public email domain like gmail.com. Check if the domain name is misspelt. Utilize virus total a free url checking website to check if the url has been reported as malicious.
Use CSRF tokens.
A CSRF token serves as a distinctive, confidential, and unpredictable code generated by the server-side application and exchanged with the client. To carry out a sensitive task, like submitting a form, the client must include the accurate CSRF token in the request. This greatly hinders an attacker from creating a legitimate request on behalf of the target. CSRF tokens in PHP can be written as follow.
$_SESSION[‘token’] = bin2hex(random_bytes(24));
Next we suggest transmit the token to the client within a hidden HTML form field, using the POST method.
<form action="/server" method="POST">
<input type="hidden" name="user_csrf_token" value="Token Value">
[...]
</form>
Ask password again when conducting important tasks.
This prevents any CSRF attack to be successful because the the attacker would not know the password. This is seen in the Security-Impossible-Level module.
Same Site Cookie.
SameSite is a security feature implemented in web browsers, which regulates the inclusion of a website’s cookies in requests that originate from other websites. Since authenticated session cookies are typically required for sensitive actions, enforcing proper SameSite restrictions can hinder attackers from initiating such actions across different sites. This policy has already been adopted by famous web portals like google in 2021.
Common flaws in CSRF token validation
- Change the request method from from
POSTtoGETto bypass validation. - Removing the entire parameter containing the token to bypass validationtion.
- CSRF token is not tied to the user session. The attacker can log in to the application using their own account, obtain a valid token.